TECHNICAL
By using the low-temperature, high-efficiency condensable heat exchange system for the recovery of waste heat, high-temperature exhaust gas from heat-generating facilities (i.e. industrial boilers, incinerators, co-generation plant, thermal power plant, etc.) is converted to low-temperature exhaust gas, thereby preventing atmospheric warming. And then, heated water is reused for co-generation heating, water boilers and supply heating for buildings, as well as agriculture and aquaculture. SOx, dust, moisture etc. are condensed (condensed water) and reduced in the heat exchange system, resulting in reducing air pollutants, preventing white smoke as well as recovering and reusing waste energy.

■ Reduction in the ratio of SOx
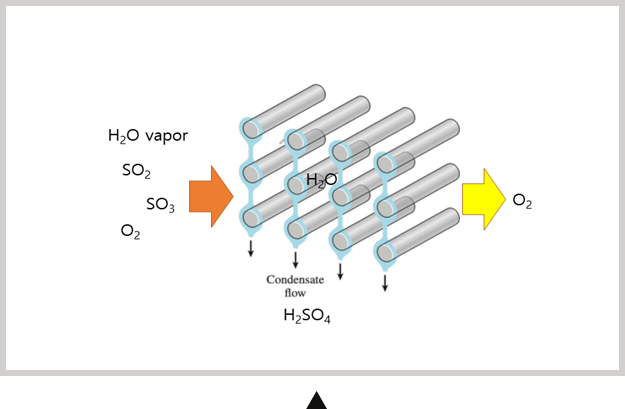
Delivery of Water-Condensed Sulfur Dioxide Gas Inside the Heat Exchange System
Sulfur present in exhaust gas reacts with oxygen to become sulfur dioxide gas, and then gets absorbed into moisture to become sulfuric acid.
Therefore, ratio of SOx in exhaust gas emissions can be reduced.
The reaction speed depends on reaction atmosphere in the heat exchange system.
■ White lead reduction
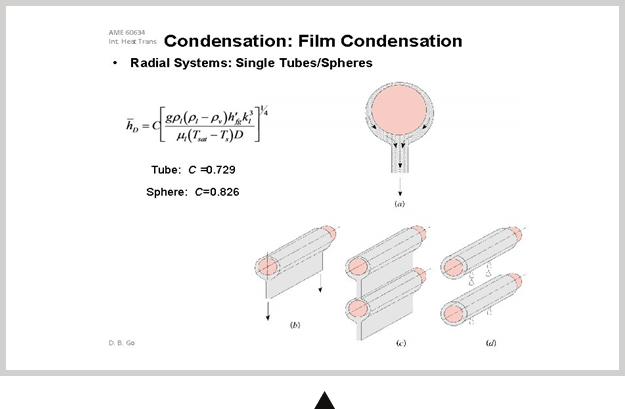
Correlation Formula of Condensed Heat Transfer Depending on the Arrangement of Tubes in the Heat Exchange System
Fine dust, sulfur dioxide and other harmful substances present in exhaust gas from the power plant, incinerator, co-generation plant, etc. are absorbed by and attached to condensed water in the heat exchange system for the recovery of waste heat. As a result, the amount of moisture present in final exhaust gas can be fully reduced.
Furthermore, exhaust gas from the final exit is emitted at a temperature of 50℃ or below, with the result that the amount of absolute moisture present in exhaust gas is minimized, and so white smoke in winter is reduced.
■ Significant reduction of fine dust content
The dust in exhaust gas is split into various sizes depending on fuels and operating conditions.
Dust present in exhaust gas is attached to and removed by moisture created in the water-condensable heat exchange system, which greatly reduces fine dust content.

Fine Dust Seen Attaching to Water-Condensed Surfaces and Being Removed in the Heat Exchange System


LUSIA ESCO CO., LTD.
LUSIA ESCO CO., LTD. / Address : 709, A, 170 Gwanggyojungang-ro, Yeongtong-gu, Suwon-si, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea